by: Lori, via the Exolab Blog
A deafening boom. A rush of air. The smell of gunpowder. And suddenly a cannonball was arcing through the air. This hypothetical cannonball, launched by Isaac Newton in a thought experiment, could be considered the shot-heard-'round-the-world heralding the arrival of the theory of gravitation.
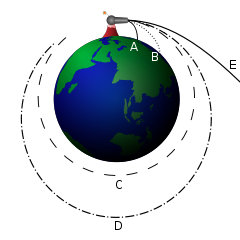

Newton reasoned if one shot a cannonball off the top of a mountain at a relatively low velocity, it would travel some distance and fall back to Earth. Faster velocities would mean the ball travels farther before it hits the ground. But of course, Newton did not stop there. What if the radius of the ball’s trajectory curve matched the radius of the Earth? The ball must keep falling, but it would never reach the ground. Essentially, it would orbit. So technically, we are falling around the sun, while the moon falls around the Earth! This particular thought experiment that led to Newton’s theory of gravity was only made known after his death. He published very few works, though they were in high demand by some scholars; most of his writings were released only posthumously. But those he did publish, like the enduring Principia in 1687, sent waves through the scholarly community.
Though there were only a few hundred copies in print, Principia could be heard discussed in coffee-houses across England. It held so much information on so many different arenas of science and mathematics, that Marquis de l'Hopital declared of Newton, “Does he eat and drink and sleep? Is he like other men?”
Indeed, Newton was not like other men. As a teenager, he was constantly inventing curious contraptions, such as a mouse-powered miniature windmill, and doodling sketches of animals, people, and shapes on the walls of his boarding home. It says something of his brilliance that in grammar school, he was never taught natural philosophy and only basic forms of arithmetic and math, and yet approximately four years later he discovered calculus! He was raised in a relatively well-off economical situation, but his life was devoid of human connection. Raised by his grandmother, his father passed away before his birth, and his mother left her only son for a new husband many years her senior. In grammar school, the other boys were everything but friendly--likely put-off by Newton's unusual intellectual superiority. Lacking friends at such a young age, he devoted all mental faculties to the pursuit of sciences, and having been scorned by his peers, he carved his name into every school bench he occupied. Later in life he would suffer from several breakdowns, causing his contemporaries to question the soundness of his intellectual abilities. Newton was thus an enigma to those around him. His wildly creative nature was incomprehensible to many, leaving him quite alone.
Through all this, Newton found solace and inspiration in God. While working on Principia, he and one of his few friends, John Locke, would exchange letters, in which Newton would dissect various Biblical passages and their meaning. Newton’s view on the physics of the universe, similar to Kepler’s, were strongly connected to his devout, yet unorthodox Christianity. He would point to God as the answer to many cosmological curiosities, such as how "dark matter" (planets, rocks) was so distinctly separated from "light matter" (the sun, stars): "I do not think explicable by mere natural causes but am forced to ascribe it to the counsel and contrivance of a voluntary Agent."
Surviving through an emotionally turbulent childhood, Newton first studied mathematics until the Great Comet of 1680 turned his eyes heavenward. Johannes Kepler's existing three laws of planetary motion provided a basis and reference for Newton to postulate his own three laws of universal motion. Newton set off to discover the force which consistently drew objects downward, toward the center of the Earth. The theory of gravitation was, consistent with the famed legend, born out of a contemplation of the trajectory of a falling apple (though the apple never actually hit him on the head), which later spawned the cannonball theory. And, if gravity worked on the Earth, why shouldn’t it be applied to the moon and the rest of the cosmos? Newton declared that the heliocentric model was in fact correct, with one caveat. It was not the Earth that revolved around the Sun, nor the Sun that revolved around the Earth, but rather, both revolving around the system's center of mass. In his own words, "the common centre of gravity of the Earth, the Sun and all the Planets is to be esteem'd the Centre of the World."
“I do not know what I may appear to the world, but to myself I seem to have been only like a boy playing on the sea-shore, and diverting myself in now and then finding a smoother pebble or a prettier shell than ordinary, whilst the great ocean of truth lay all undiscovered before me.”
Isaac Newton
Comments